
In today's rapidly advancing industrial landscape, the need for precision and efficiency in metal manufacturing has never been more critical. Among the various techniques available, Metal Laser Cutting stands out as a revolutionary approach that combines speed, accuracy, and versatility. This cutting-edge technology utilizes high-powered laser beams to achieve clean and precise cuts in a wide range of metal materials, making it an indispensable tool in sectors such as automotive, aerospace, and construction.
The advantages of Metal Laser Cutting are numerous. It not only enhances the quality of cuts, minimizing waste and reducing the need for secondary operations, but also allows for intricate designs that are difficult to achieve with traditional cutting methods. As industries push for higher production standards and leaner processes, the adoption of advanced laser cutting techniques becomes essential. By examining the various Metal Laser Cutting methods and their applications, we can better understand how they contribute to greater operational efficiency and product excellence in modern manufacturing.

Metal laser cutting has evolved significantly, offering various techniques that optimize precision and efficiency in industrial applications. The primary methods include CO2 laser cutting, fiber laser cutting, and disc laser cutting. Each technique is tailored to specific materials and thicknesses, providing manufacturers with flexibility in their processing requirements. According to a recent industry report, the global market for laser cutting is projected to reach $4.13 billion by 2025, driven by the increasing demand for precision-engineered components across sectors like automotive, aerospace, and electronics.
CO2 laser cutting is known for its versatility and ability to cut through a wide range of materials, including non-metals. It operates at high speeds and delivers clean edges, making it suitable for intricate designs. On the other hand, fiber laser cutting has gained prominence due to its higher efficiency and lower operational costs. Data from industry analyses show that fiber lasers outperform CO2 lasers in speed and energy consumption, particularly for thinner metals, resulting in up to 60% reduced operational costs. Furthermore, disc laser cutting has emerged as a cutting-edge technique, offering superior quality and the ability to cut through thicker materials while maintaining high-speed operations. As manufacturers continue to adopt these advanced laser cutting techniques, the emphasis on efficiency and precision remains crucial to staying competitive in the dynamic industrial landscape.
| Technique | Material Types | Cutting Thickness (mm) | Speed (m/min) | Precision (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CO2 Laser Cutting | Mild Steel, Stainless Steel, Aluminum | 0.5 - 25 | 5 - 10 | ±0.1 |
| Fiber Laser Cutting | Stainless Steel, Brass, Copper | 0.5 - 20 | 10 - 20 | ±0.05 |
| Nd:YAG Laser Cutting | Aluminum, Steel | 0.5 - 15 | 2 - 8 | ±0.1 |
| Ultrafast Laser Cutting | Metal Foils, Thin Sheets | 0.1 - 5 | 15 - 30 | ±0.01 |
Laser cutting has revolutionized the metal fabrication industry, presenting a host of advantages over traditional cutting methods. One of the primary benefits is precision. Laser cutting technology allows for intricate designs and fine details to be achieved with remarkable accuracy. Unlike mechanical cutting, which can produce burrs and require subsequent finishing processes, laser cutting delivers a clean edge, minimizing the need for additional work. This level of detail is particularly advantageous in industries that require strict tolerances, such as aerospace and automotive manufacturing.
Efficiency is another significant advantage of laser cutting. Traditional cutting methods often involve slower speeds and can be more labor-intensive, leading to increased production times and costs. In contrast, laser cutting systems can operate at higher speeds, significantly reducing cycle times. Additionally, they require less manual intervention, allowing operators to focus on value-added tasks rather than overseeing repetitive cutting operations. As a result, businesses benefit from both reduced labor costs and improved throughput, making laser cutting a more viable option for modern manufacturing needs.
This chart illustrates the performance of metal laser cutting techniques versus traditional cutting methods across key metrics. Laser cutting techniques generally offer higher speeds and precision while requiring much lower setup times compared to traditional methods.
In the domain of metal laser cutting, precision is paramount to achieving high-quality results. Key parameters that influence precision include laser power, cutting speed, and assist gas type. Laser power directly impacts the cutting capability and depth; higher wattage can enhance the cutting speed and effectiveness, particularly in thicker materials. However, finding the optimal power setting is crucial, as excessive power can lead to burn marks and reduced edge quality.
Cutting speed is another critical factor that affects the accuracy of cuts. A balanced speed ensures that the laser has adequate time to penetrate the material without undue thermal distortion. Adjusting the cutting speed according to the thickness and type of metal not only improves precision but also enhances the efficiency of the operation. Additionally, the choice of assist gas, whether oxygen or nitrogen, plays a significant role in the quality of the cut. Oxygen can provide a faster cutting process in certain materials, while nitrogen helps in achieving clean edges and minimizing oxidation.
Furthermore, proper focusing of the laser beam is essential for maintaining precision. The focus point must be adjusted correctly to match the thickness of the metal being cut. A well-focused beam allows for cleaner cuts and reduced kerf width, thereby improving the fit of fabricated parts. By meticulously controlling these parameters, manufacturers can achieve optimal operational efficiency while ensuring the highest standards of precision in metal laser cutting.

Innovative technologies have significantly advanced metal laser cutting, enhancing both precision and efficiency. Recent industry reports indicate that the global laser cutting market is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of approximately 5.5% from 2021 to 2028, driven by improvements in laser cutting techniques and materials used. One of the most noteworthy advancements is the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning algorithms, which enable real-time monitoring and adjustment of cutting parameters. This leads to a reduction in material waste and enhances the overall efficiency of the cutting process.
Additionally, the introduction of fiber laser technology has revolutionized metal cutting by offering higher power output and better beam quality compared to traditional CO2 lasers. According to a recent market analysis, fiber lasers can increase cutting speeds by up to 30%, while also providing superior energy efficiency. This transition not only accelerates production time but also reduces operational costs, making fiber lasers a preferred choice for many manufacturers. As companies continue to adopt these innovative technologies, the landscape of metal laser cutting is evolving, paving the way for greater productivity and precision in the industry.
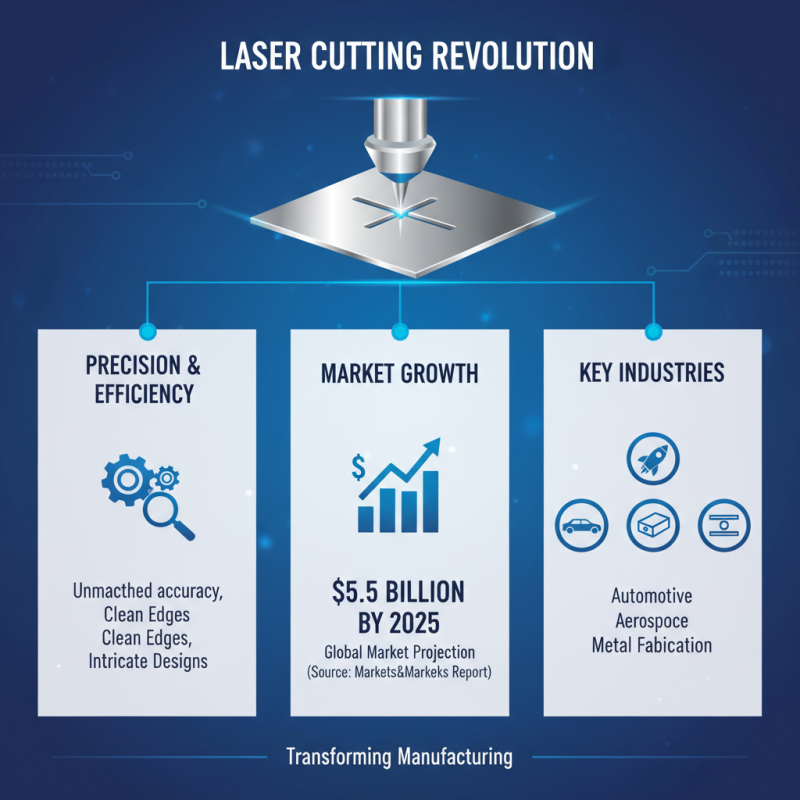
Laser cutting technology has revolutionized manufacturing across various industries, providing unmatched precision and efficiency. According to a report by MarketsandMarkets, the global laser cutting market is projected to reach $5.5 billion by 2025, with a significant portion of this growth driven by its applications in diverse sectors such as automotive, aerospace, and metal fabrication. These industries require high precision components, where laser cutting excels by offering clean edges and intricate designs that traditional cutting methods struggle to achieve.
In the automotive industry, laser cutting is utilized for manufacturing parts like chassis components and brackets, as it allows for the rapid production of complex geometries without compromising on strength or performance. The aerospace sector benefits greatly from this technology as well, as lightweight and durable components are critical. The ability to cut through materials such as titanium and aluminum with high accuracy reduces material waste and manufacturing time, enhancing overall efficiency. As reported by the International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, companies using laser cutting techniques have seen reductions in production costs by up to 30%, while dramatically improving their product turnaround times.
Manufacturers in the metal fabrication sector similarly leverage laser cutting for applications ranging from signage to intricate artistic designs. The flexibility and adaptability of laser cutting technology support small to large-scale production runs, making it an essential tool for both custom fabricators and high-volume manufacturers. The increasing need for customization across various industries further drives the demand for advanced laser cutting solutions, highlighting the technology’s role in modern manufacturing processes.






